SEO for Starters

The sooner you step into the world of digital technology and marketing, the complexer SEO (search engine optimization) practices and Google algorithm appear to you. Forget about all your doubts and previous complicated or contradictory knowledge you have gained while researching here and there. If you are an SEO starter and looking up to build your career as an SEO expert, this guide is useful to you.
Keywords Research
You must conduct a thorough keyword research to discover actual search terms used by the users to find solutions to their problems, answers to their questions, and service providers for their requirements. Because a user not always writes a complete sentence to get answers, Google has recognised a set of words (keywords) which are frequently searched by the users.
Here’s an example:
If the user wants to shop a blue pen online, instead of writing “I want to shop a blue pen online”, he would write “blue pen online”. And even if he doesn’t, Google would identify his purpose of research as “buy/sell/shop blue pen online”.

Know all inside-outs of your business by a critical and thorough keyword research. Your keyword research begins right from checking and evaluating your competitors’ website and ends nowhere. If you want to become an SEO expert, then be prepared for endless hunt for business website related keywords!
- Track Your Competitor
Map down your online competitors and start analyzing their websites. If you own an ecommerce business of stationery, then make a list of all the websites ranking in top 10 or 15 search engine results. Begin looking for the keywords that they have used in meta title, meta description and content.
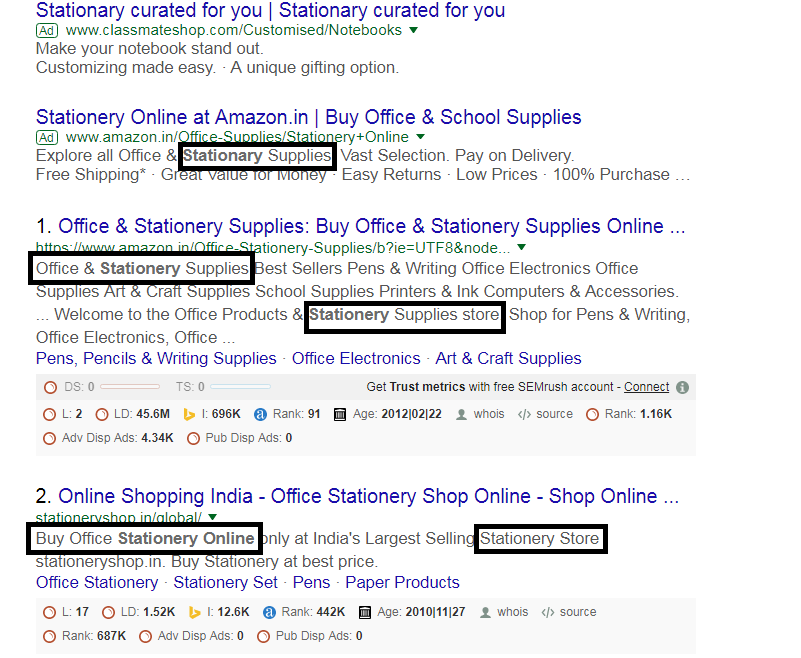
As shown above, buy office stationery online, stationery store, stationery supplies store, office & stationery supplies are the keywords that show 96 % match with stationery online as the user’s query.
- Head terms vs long tail keywords
The head terms/root words are relevant for any search engine to respond to your query appropriately. Head terms are the root or basic word phrases that constitute a long tail keyword. See below how long tail keywords are derived-
Head Term/Root Word: Office Stationery
Long Tail Keyword: Buy Office Stationery online
: Buy Office Stationery Items online
: Bulk Office Stationery Supplies
It is recommended that you choose long tail keywords to do SEO of your website as the head terms are more competitive and reduce your website ranking. By making those precise, and to the point for the users, you get relevant traffic even if your website doesn’t rank in top 3 results. Not the basic or generic keywords would get you the relevant traffic always.
Suppose you have fetched the keyword “writing thesis” in your blog post, less probability is there that they are looking for thesis writing services but more who are looking for the guidance on “how to write a thesis”. Can you detect the difference?
- Leverage LSI keywords
Latent semantic indexing or LSI keywords are the auto-generated keywords that semantically related to your head term or long tail keyword. Let us do an activity!
Search for “Girls shoes” on Google. Scroll down and down till the end of the SERP page.
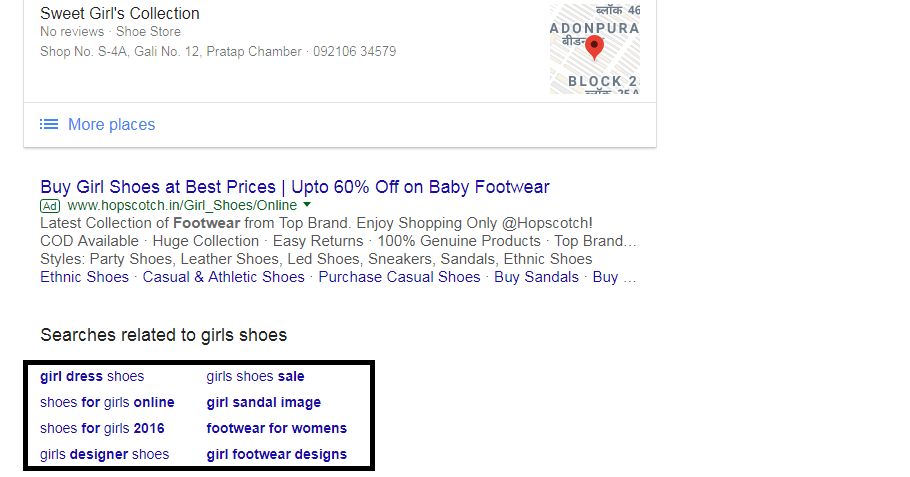
What do you see? A list of random words similar to your search termed in meaning- these keywords are called LSI keywords which Google picks and shows randomly to the user.
You can use these keywords and fetch them in your website’s content and blogs accordingly along with creating a meaningful whole.
On-page SEO
On-page or on-site SEO refers to optimizing a website’s web pages, meta-content and the website content. The optimization, improvisation, and changes you make on your website would be shown on the live version of website, indexed and considered by Google when it comes to rank your website.
So, where do we make the changes or what elements of a website do we optimize for search engines?
- Meta-title:
The head of the document is defined by HTML code. It contains the data about the content of the web page or blog post. This meta title tells the reader as well as the search engine what a particular web page is all about. In the HTML coding, meta title is defined as:
<title> How to write a PhD thesis</title>
Users would see only the title as “How to write a PhD thesis” but the search engines would see it as <Meta-title starts> How to write a PhD thesis </Meta-title ends>.
Below is an example of how users see the meta-title.
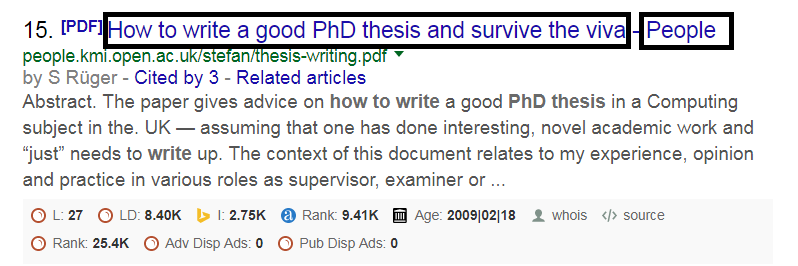
Users would see what your web page, blog post or forum thread is all about while the search engines would use it for indexing purpose. But how to use the meta-title to improve Google ranking? Ideally, it should be structured and defined in the head of your HTML coding as:
Keyword (Primary)|Brand/Website’s Name
It would be like:
How to write a PhD Thesis|ABC
Here ABC is your brand/website’s name. The title should be crisp, short, and relevant in no more than 60-70 characters for uplifting the overall rankings of your website on search engines and the visibility of your website.
- Meta-description
Where the meta-title gives a name to your web page, blog post, or other content published online, meta-description provides a brief overview of the content prima-facie.
Users see it in the form of snippet having an explanation or summary of what the content, web page, blog or product. Where Google recommends giving the precise details and information of the content in meta-description, you can use it for SEO purpose as well. You can fetch the keywords in the meta-description in a natural way but do not exceed the limit of 320 characters (formerly, it was 160 but Google has recently extended the character limit).
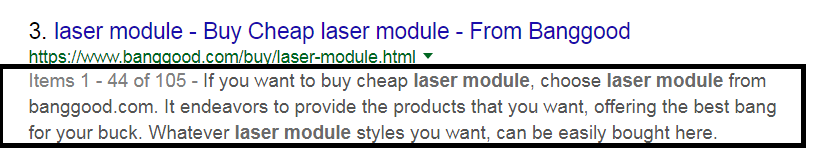
Not to forget, much of the rise and fall in your website ranking depends on the quality of the meta-title and description which you label to your website.
- Heading Tags
In this guide, we have used heading levels in MS-word to differentiate the main heading (highlighted as bold, enlarged in font size, and variant in font type) and the consequent sub-headings so that you read and understand the sub-sections clearly.
Similarly, the headings are defined in a website using various heading tags <h1, h2, h3…> to highlight and segregate the headings, sub-headings, and content of a web page. These tags are inserted in the HTML coding of a website to give a neat and defined look to the content for user’s ease.
You can give an endless number of headings in a website using these heading tags. However, this must be noted that <h1>, <h2>, <h3>…etc. would keep decreasing the size of the HTML headings with every successive tag used.
<h1> Heading 1 </h1>
<h2>Heading 2 </h2>
<h3> Heading 3 </h3>
<h4> Heading 4 </h4>
Heading tags are boon in SEO practices if the keywords are naturally fetched in the content headings which would let Google index and identify as the answer to the user’s query.
- Sitemap
Every search engine, such as Bing, Google, Baidu has its computerised program called web crawler which explores the content and information of a website. The collected data is delivered to search engine by crawler so that the website can be indexed into the database of search engine.
Googlebot is one such crawler that reads the content defined in website coding and delivers the same to Google. But how crawler access this content on your website? This is done by your website’s XML (Extensible Markup Language) sitemap you prepare and submit it to the search engine. (For Google, you must submit the XML sitemap through Google Search Console)
All web elements, content, sections, and resources of a website that you like Google to crawl and index are listed in the XML sitemap with URLs. Other details to include in your XML sitemap are:
- URL of website (compulsory)
- When website was last updated (compulsory)
- How often the web page is updated (Optional)
- Scale the importance of a particular web page in your website (optional)
It delivers the metadata to search engines which include the information and details regarding the updations in website content, URL, change in page, redesigned website etc. Therefore, if you want to tell Google about the latest modifications in the content or design of your website, it is recommended that you submit XML sitemap to Google or other search engine.
How to create XML sitemap?
You can create XML sitemap manually or through the XML sitemap generator software freely available online.
Manual Method: To generate XML sitemap, use the following code:

You can locate XML sitemap of your website through the URL www.websitename.com/sitemap.xml
Using Online Tools: Many free and easy to use tools are available online to create XML sitemaps. Following is a list:
- www.smallseotools.com
- www.xmlsitemapgenerator.org
- www.screamingfrog.co.uk
Apart from this purpose, sitemap is useful for the website visitors also. It helps them get directions to explore your website if it has many web pages or complex resources that is tough for him to find. But XML sitemaps are not built for users as the XML protocol cannot be understand by a human user. Therefore, you should prepare an HTML sitemap and publish it on your website for users’ ease as per the theme and design of your website.
- URL Structure
Uniform resource locator or URL is your website’s unique address through which users can locate your website on internet. Not significant but yes; the structure of the URL holds a value in your website ranking. A URL which is simple, easy to remember and contains a main keyword in it become comprehensible for both the user and the search engines.
If you create a new web page that doesn’t reflect what specific page is opened, the user and search engine would feel lost. Refer to the example below:
Inapt URL Structure: www.abc.com/20%7c6thywdoklswwahn40%Hfc
This URL is tough to memorize for the user. These are usually auto-generated permalinks which can be redefined manually Therefore, it is recommended that you keep the length of website’s URL to only 2,083 characters. See the suitable URL below:
Apt URL Structure: www.abc.com/writingservices.php
It is also important that you keep a track on the auto-generated duplicate URLs of a particular web page. Multiple URLs refer to the same web page would result into canonical issue which means search engines can index all such multiple or duplicate URLs for a single page. Under the URL canonicalisation issue, your website can be accessed by all the following URLs:
- http://abc.com
- http://abc.html
- http://www.abc.com
You can keep a track on such URL issues, you can use SEO Check & audit tools such as seositecheckup.com or SEOquake. These tools would help you create search engine friendly urls.
- Image Alt Tags
Whenever you use images in your blog post, article, or website content, you must introduce it to the web spider or crawler. Because crawler is an automated program that could not see the image but only can read it through the code, you must define the image in the code using image Alt tag.
One can define the image using the code given below:
<img src=”image-path” alt=”keyword”>
Here keyword would tell the Googlebot (crawler) what the image is all about. This plays an important role in driving relevant traffic to your website. Suppose a user is interested to see the images of a product that you offer, and you have used the suitable and relevant keyword in image Alt tag, then your image might be ranked in the top in Google’s search image results. Therefore, using image Alt tags has become a significant practice.
- Content: Quality and Freshness
Content is a prerequisite for doing SEO effectively! Because search engines today work on the quality content and relevant keywords, the content that you published online should be informative and precise. Content doesn’t only mean the article, blogs, or website content but includes the images, infographics, how-to videos, business videos, etc. But how do you judge its quality? Following are the parameters to help you evaluate the relevancy and overall quality of your SEO content:
- Relevant content for the target readership/audience
- Contains knowledge of prime importance
- Less keywords used in the content
- Only relevant keywords fetched in the content
- Content with no keyword stuffing
- Content which speaks explicitly about the topic/issue
- Every sentence of the content should behave as a meaningful whole
- Source Code Optimization
Search engines, at times, do consider the source code of your website as one of the ranking factors. Therefore, it is important that you optimize your website’s source code by keeping it well-defined and clean. Eliminate the fragmented codes, and the excessive white spaces or characters left out in between the code which adds no value to website’s operations. If you do not want a few web pages to be indexed or accessed by web spider, then make sure you disavow the same in HTML coding. Try to incorporate more text-versions of your content in the source code as the search engines can’t access the flash content, video or images. Define your website’s content and resources by breaking it all into microdata using HTML tags such as heading, image Alt, title, description tag etc. Not only this would benefit you to keep your website search engine friendly but also it might get ranked as featured or rich snippet.
- Page Speed
What is the total time taken by your website to load its web pages on mobile or desktop when the request was made is called page speed. Page speed is considered as an important factor in SEO because Google doesn’t like his visitors to wait for you. So, if your website has poor or slow page speed, your ranking would be increased (might shift from 1st position to 5th or 10th to 50th in SERP). You can scale your website’s page speed through the SEO audit tools or as per the scale given below:
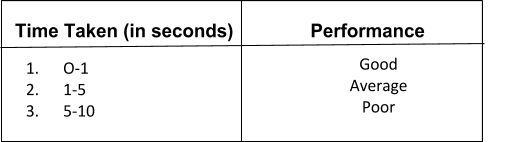
A search engine friendly website is the one that is quick in loading its web pages, or responding to all other requests made by the user or crawler. You can check the page speed of your website through Google’s Page Speed Optimization Insights which is freely available.
- Structured markup code
Using Schema markup, you can give your website a considerable hike in rankings and showcase your product or service. Unlike the usual text versions, schema (structured markup code) represents the data into a well-defined format that increases its presentation and visibility scope in search engines.
What is this well-defined format? These are mainly the HTML tags to identify item type, rating, and review of the product or services offered. Using schema, the data is presented by search engines as visualised below:
You can generate schema code for your website at Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper.
Off-Page SEO
Off -page optimization or SEO of your website means that you do not make any changes, improvements in the live version of your website to improve its search engine rankings (like you in on-page optimization). Off-page means you build quality backlinks to your website on anywhere on internet. Such quality backlinks give a boost to your website or web page rankings in SERPs. Here are the basic off-page SEO activities that help you do an effective optimization:
- Link Search Strategies
To build backlinks to your website, you should not rely on any third-party platform that could give you the relevant traffic. Remember, your aim of link-building is to drive relevant and useful traffic to your website and not simply to improve search engine rankings. For this, you must search the reliable websites, web directories, forums, blog posts, and content distribution platforms that are niche to your business or website. You have to research on what makes a website reliable, trustworthy, and having good reputation amongst the audience or readership where you can post your link.
The easy way to get a hold of such resources is to map down where your competitors have made their backlinks using backlink checker tools. You can subscribe to the tools such as Majestic.com, ahrefs.com, MozRank, etc., for tracking or finding the relevant sources where you can build quality backlinks. This type of link would be called backlink and add prominence to your website ranking. Some good platforms having strong audience include Medium.com, indianyellowpages.net, storify.com, visually.com, etc.
- Importance of DA/PA
Domain Authority (DA) and Page Authority (PA) are two main parameters on which you should judge the quality of the website or platform to build backlinks. Domain authority is a score (0-100) both developed and given by Moz to a website to reflect the overall strength of a website’s domain to rank top on search engine results page based on the link counts. Similarly, Page Authority measures the strength of a particular web page that can easily rank on search engines. Apart from the link counts, it also gives an idea of how strong the readership or audience is for a website, blog, page, forum, etc. You can check any website’s DA or PA using Mozbar (Toolbar designed by Moz). If the score lies above 40, the platform acts as a good platform to build your website’s backlink on.
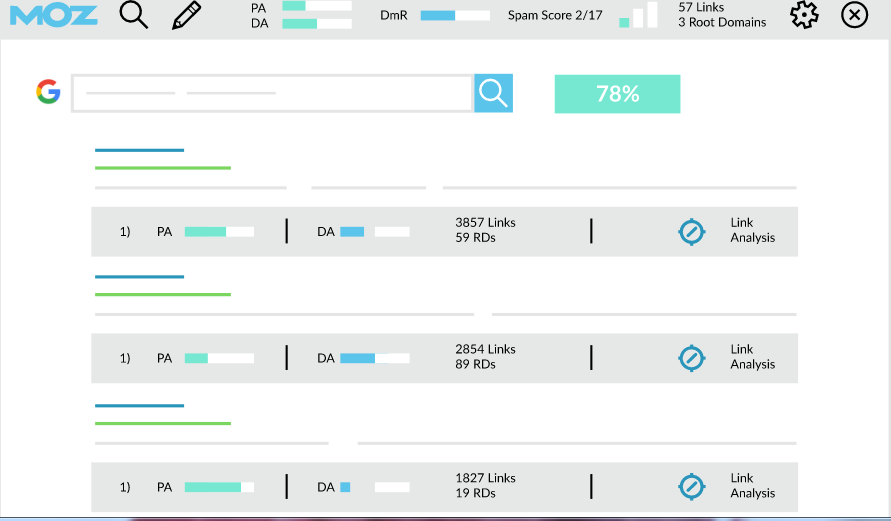
Please note that DA & PA are not only metrics that you should rely on for link-building as the website having 25 DA, or PA has a good readership and visibility across the internet. It is still recommended that you keep this score in consideration while building quality backlinks.
- Do-Follow & No-Follow Links
No-follow and Do-follow are the HTML attributes that guide the search engines whether the inbound links of a website should be followed, tracked, considered or not to decide on the page or website ranking. A do-follow attribute is used to recommend Google (in particular) to consider the quality of the link and improve the website’s (which has been linked to a third-party platform) search engine rankings and vice versa for a no-follow attribute.
Here is how you define a no-follow link:
<a href=”http://abc.com/” rel=”nofollow”>xyz</a>
And how to define a do-follow link:
<a href=”http://abc.com/”>xyz</a>
While humans can reach the no-follow links, Googlebot or crawler cannot. All the backlinks you create are automatically set to do-follow attribute for the search engine to tell the passing of link juice (transaction of traffic from one website to other).
- Links Caching
Despite doing effective off-page optimization of your website, it might be possible that there is improvement observed in your search engine rankings. One of the common reasons could be the inability of the crawlers to acknowledge the backlinks you have created. Optimization means that you are updating your website and backlinks on a regular basis which crawler is tracking through links caching. It is important that you track if the search engine is caching your backlinks or not.
If not, then you should spread the link you made using multiple platforms to let search engine naturally cache. Else, you can submit the backlinks you create through Google’s Submit URL tool.

